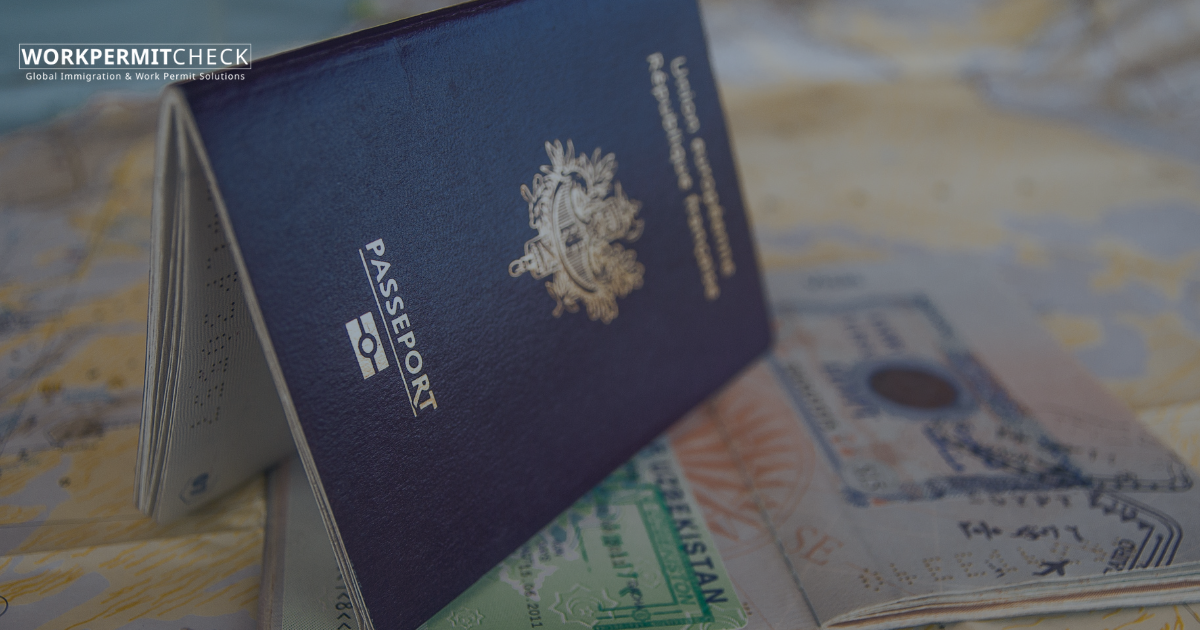
Foreign nationals working in Australia are subject to Australian income tax laws, just like local employees. Whether you are on a temporary work visa or a permanent skilled visa, you must meet certain tax obligations under the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) regulations.
Understanding your tax status, rates, and reporting duties is essential to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with Australian law.
Determining Tax Residency Status
The first step in understanding your tax obligations is identifying your tax residency status.?The ATO classifies individuals as either:
• Australian residents for tax purposes, or
• Foreign (non-resident) workers
Residency is determined by factors such as:
• The length of stay in Australia
• Employment contract and visa duration
• Whether you reside and work primarily in Australia
Generally, those living and working in Australia for more than six months are considered tax residents, even if they hold a temporary visa.
Income Tax for Foreign Workers
All foreign workers must declare and pay tax on income earned in Australia. The main points include:
• Tax File Number (TFN):?You must obtain a TFN from the ATO to be legally employed and ensure correct tax withholding.
• Employer Withholding:?Your employer will deduct Pay As You Go (PAYG) tax from your salary before payment.
• Tax Rates:
? Residents for tax purposes benefit from progressive tax rates and a tax-free threshold (currently AUD 18,200).
? Non-residents do not receive a tax-free threshold and pay a flat rate starting from the first dollar earned.
• Superannuation Contributions:?Employers are required to contribute to a superannuation fund (retirement savings) on behalf of eligible employees, including foreign workers.
Lodging a Tax Return
Foreign workers must file an annual tax return with the ATO, usually between 1 July and 31 October for the previous financial year.
This process allows you to:
• Report all income earned in Australia
• Claim any eligible deductions or offsets
• Receive a tax refund, if applicable
Returns can be lodged online through myGov, via an Australian tax agent, or by mail.
Double Taxation Agreements (DTA)
Australia has tax treaties with many countries to prevent double taxation on the same income.?If your home country has a DTA with Australia, you may be able to:
• Claim a foreign income tax offset, or
• Avoid paying tax twice on the same earnings
Check the specific provisions of your home country’s agreement with Australia on the ATO website.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to meet your tax obligations can result in:
• Penalties, interest charges, or fines
• Difficulty renewing or extending your visa
• Issues with future immigration or residency applications
Always keep records of your income, payslips, and tax documents during your stay.
Verify Your Work Permit Before Employment
Before starting work in Australia, it’s crucial to verify that your work permit or visa is authentic and issued by the Department of Home Affairs. Using WorkPermitCheck.com, you can confirm the legitimacy of your work authorization and avoid employment-related risks.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute tax or legal advice. WorkPermitCheck.com provides independent verification services to help users confirm the authenticity of work permits and employment documents. For official tax guidance, please consult the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) or a registered tax advisor.
October 9, 2025